HOW TO DESCRIBE ROS NODES USING THE LANGUAGE
Component models have two types of extensions, either .ros1 for ROS version 1 packages and .ros2 for ROS 2 packages. In both cases the language allows to describe package that contains ROS nodes and their interfaces. To create a new model, you can easily just create a new file with the correct extension, the RosTooling environment will automatically recognize it and make use of its related features for the textual editor.
ROS (1)
In ros1 the grammar is as follows:
my_awesome_pkg: #Name of the package
**fromGitRepo: ** "http://github.com/MyAccount/RepoName:BranchName" # Optional, Git reopsitory path that contains the source code
**artifacts:**
awesome: # Name of the artifact (as it is named in the CMakeLists)
**node:** awesome_node # Name of the node
**publishers:** # (Optional) List of publishers
awesome_pub:
**type:** "std_msgs/msg/Bool"
**subscribers:** # (Optional) List of subscribers
awesome_sub:
**type:** "std_msgs/msg/Bool"
**serviceclients:** # (Optional) List of service clients
awesome_client:
**type:** "std_srvs/srv/Empty"
**serviceservers:** # (Optional) List of service servers
awesome_server:
**type:** "std_srvs/srv/Empty"
**actionclients:** # (Optional) List of action clients
awesome_action:
**type:** "control_msgs/action/JointTrajectory"
**actionservers:** # (Optional) List of action servers
awesome_action:
**type:** "control_msgs/action/JointTrajectory"
**parameters:** # (Optional) List of parameters
awesome_param:
**type:** String
**default:** "Hello"
The format is based on YAML. All the words marked in the template with ‘**’ are keywords that compose the model, they can’t be modified.
See the following model example for the known teleop ROS package:
teleop:
artifacts:
teleop_twist_joy_node:
node: teleop_twist_joy_node
publishers:
cmd_vel:
type: "geometry_msgs/msg/Twist"
subscribers:
joy:
type:"sensor_msgs/msg/Joy"
ROS 2
The ros2 grammar is as follows:
my_awesome_pkg:
**fromGitRepo: ** "http://github.com/MyAccount/RepoName:BranchName"
**artifacts:**
awesome:
**node:** awesome_node
**publishers:**
awesome_pub:
**type:** "std_msgs/msg/Bool"
**qos:**
**depth:** 10
**durability:** volatile
**history:** keep_all
**profile:** default_qos
**reliability:** best_effort
**subscribers:**
awesome_sub:
**type:** "std_msgs/msg/Bool"
**qos:**
**depth:** 10
**durability:** transient_local
**history:** keep_last
**profile:** sensor_qos
**reliability:** reliable
**serviceclients:**
awesome_client:
**type:** "std_srvs/srv/Empty"
**qos:**
**depth:** 10
**durability:** volatile
**history:** keep_all
**profile:** services_qos
**reliability:** best_effort
**serviceservers:**
awesome_server:
**type:** "std_srvs/srv/Empty"
**qos:**
**depth:** 10
**durability:** volatile
**history:** keep_all
**profile:** services_qos
**reliability:** best_effort
**actionclients:**
awesome_action:
**type:** "control_msgs/action/JointTrajectory"
**qos:**
**depth:** 10
**durability:** volatile
**history:** keep_all
**profile:** default_qos
**reliability:** best_effort
**actionservers:**
awesome_action:
**type:** "control_msgs/action/JointTrajectory"
**qos:**
**depth:** 10
**durability:** volatile
**history:** keep_all
**profile:** default_qos
**reliability:** best_effort
**parameters:**
awesome_param:
**type:** String
**default:** "Hello"
**qos:**
**depth:** 10
**durability:** volatile
**history:** keep_all
**profile:** parameter_qos
**reliability:** best_effort
The only remarkable difference with the ROS 1 model is that the quality of service can be defined for all the interfaces. The quality of service attributes are optional and they allow the following options:
- depth: it must be an integer.
- durability: volatile / transient_local
- history: keep_all / keep_last
- profile: default_qos / sensor_qos / services_qos/ parameter_qos
- reliability: best_effort / reliable
The type of supported parameters are:
- Boolean
- Double
- String
- Integer
- Base64
- List [Type, Type]
- Array [Type]
- Struct [Name Type, Name Type]
For more details about parameters, please check the site about the parameters definition.
See the following example for the arucos_ros driver:
aruco_ros:
fromGitRepo: "https://github.com/pal-robotics/aruco_ros.git:humble-devel"
artifacts:
marker_publisher:
node: marker_publisher
subscribers:
image_raw:
type: "sensor_msgs/msg/Image"
publishers:
debug:
type: "sensor_msgs/msg/Image"
markers:
type: "aruco_msgs/msg/MarkerArray"
markers_list:
type: "std_msgs/msg/UInt32MultiArray"
result:
type: "sensor_msgs/msg/Image"
parameters:
camera_frame:
type: String
image_is_rectified:
type: Boolean
marker_size:
type: Double
reference_frame:
type: String
raw_image_topic:
type: String
use_camera_info:
type: Boolean
use_sim_time:
type: Boolean
camera_info_topic:
type: String
Textual model editor
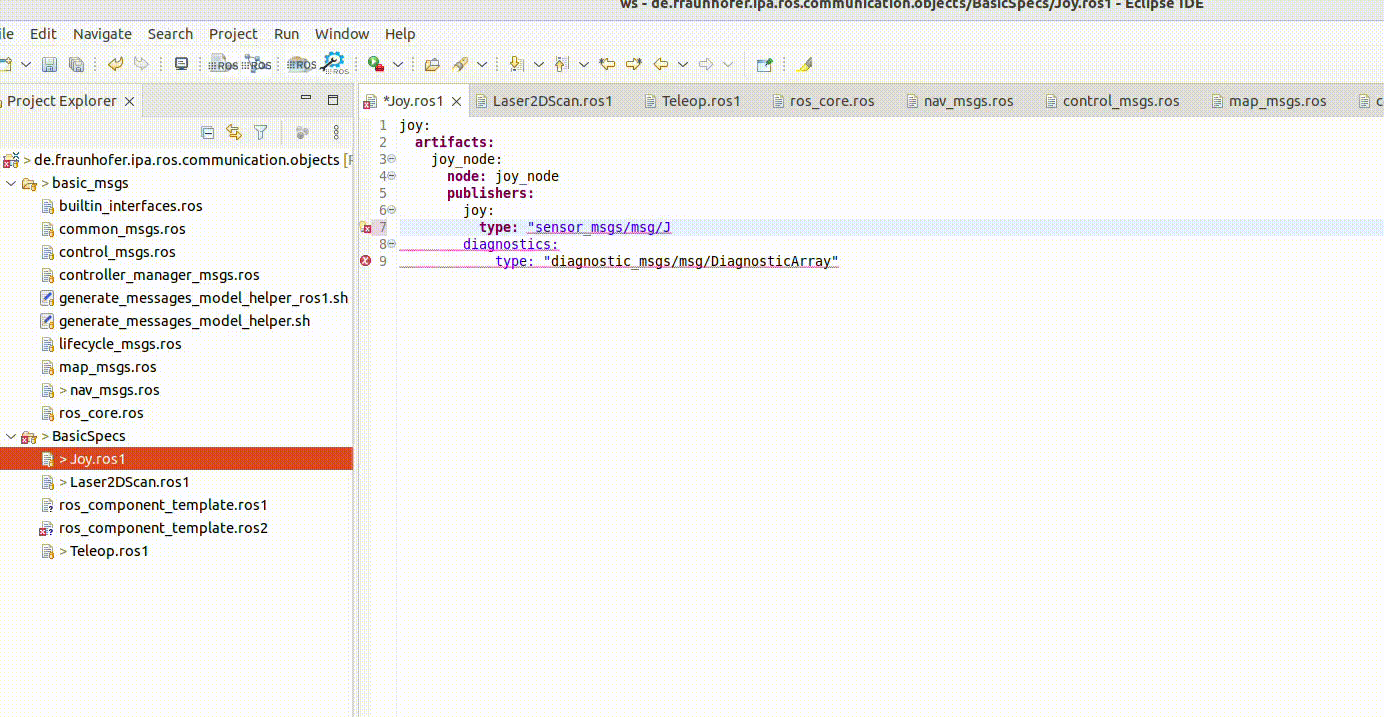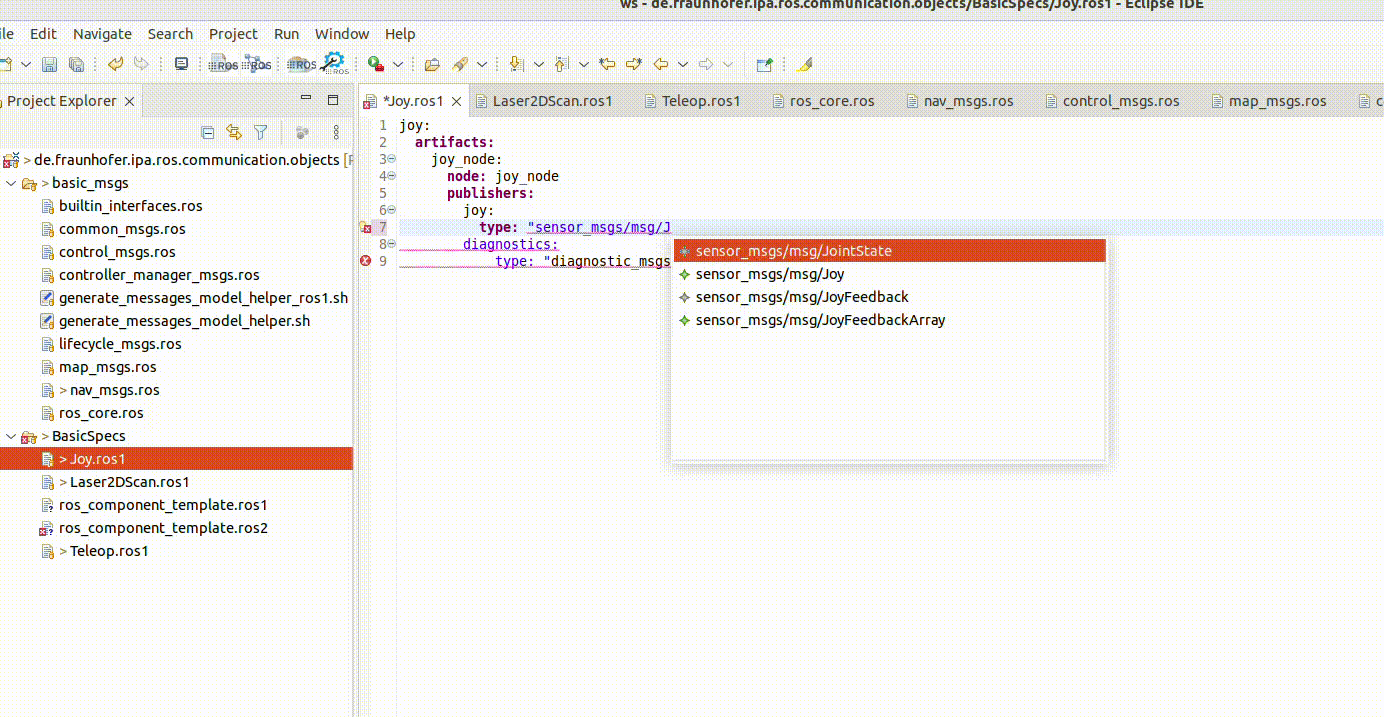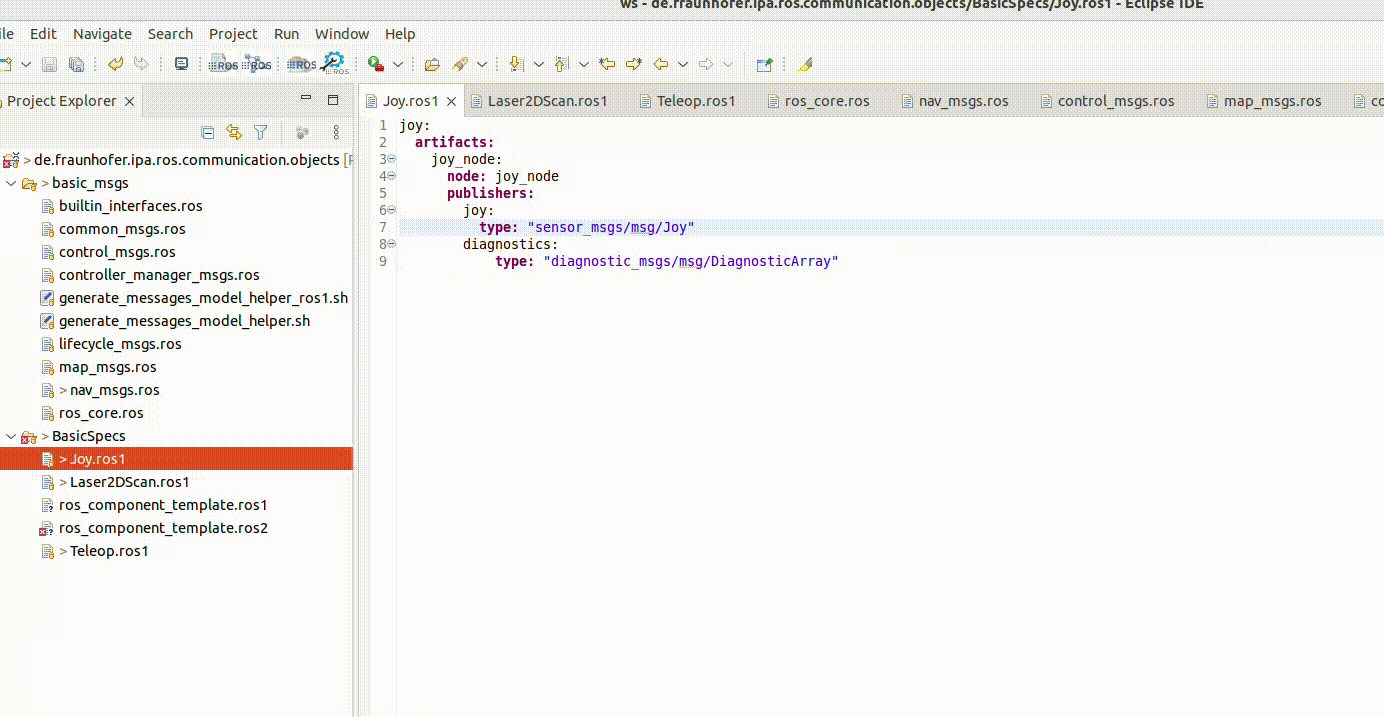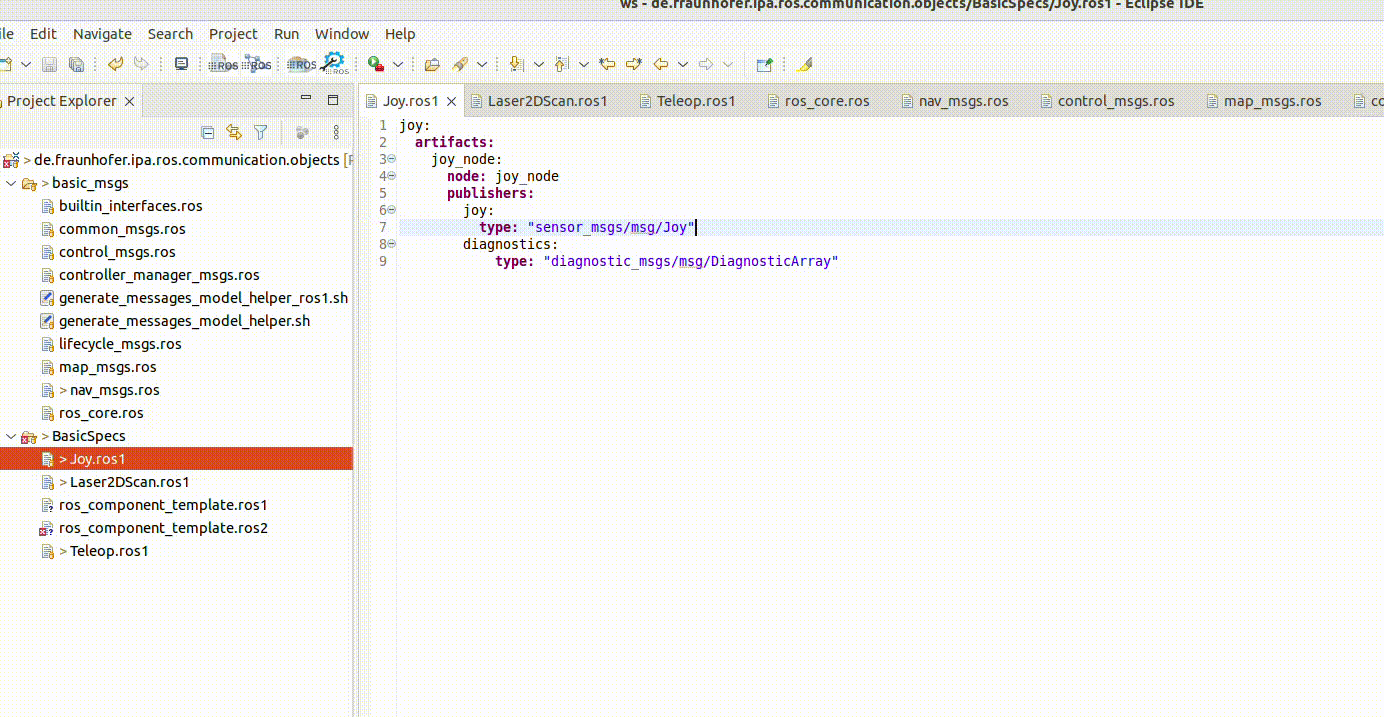
The textual editor contains a checker embedded, for example:
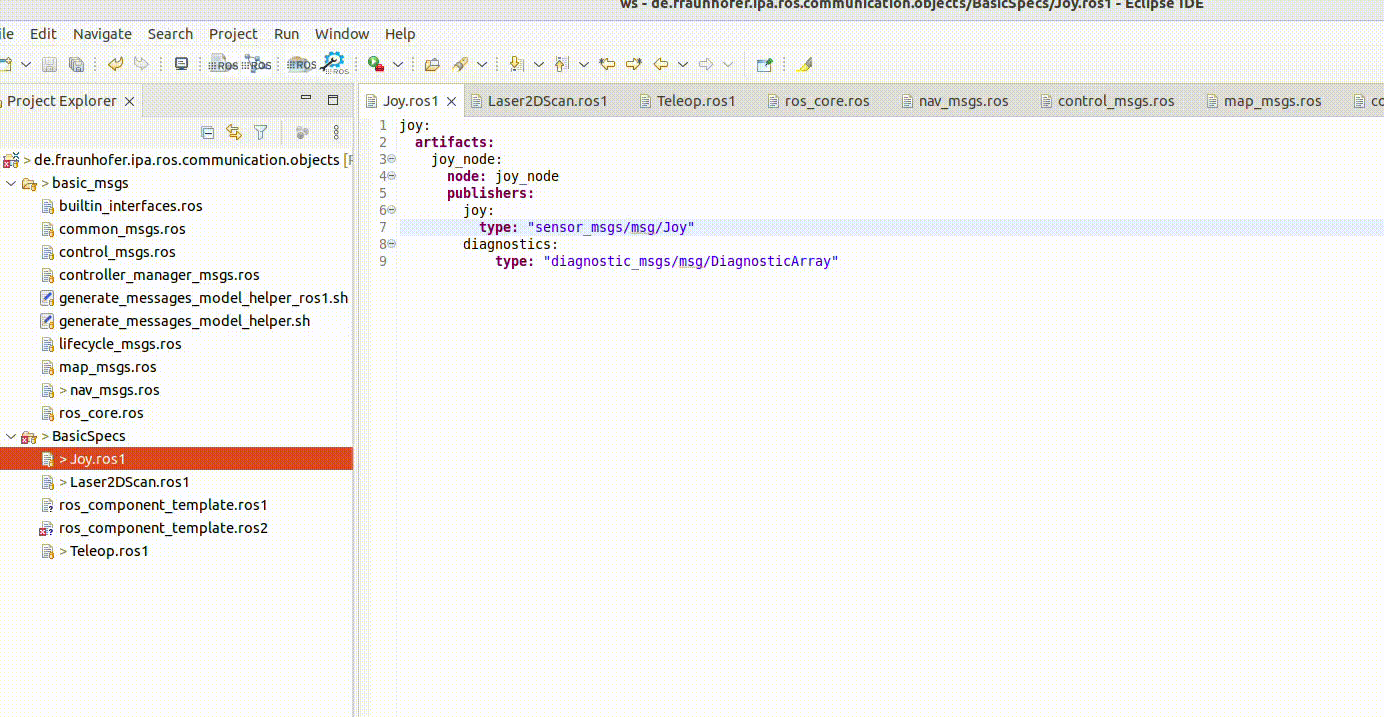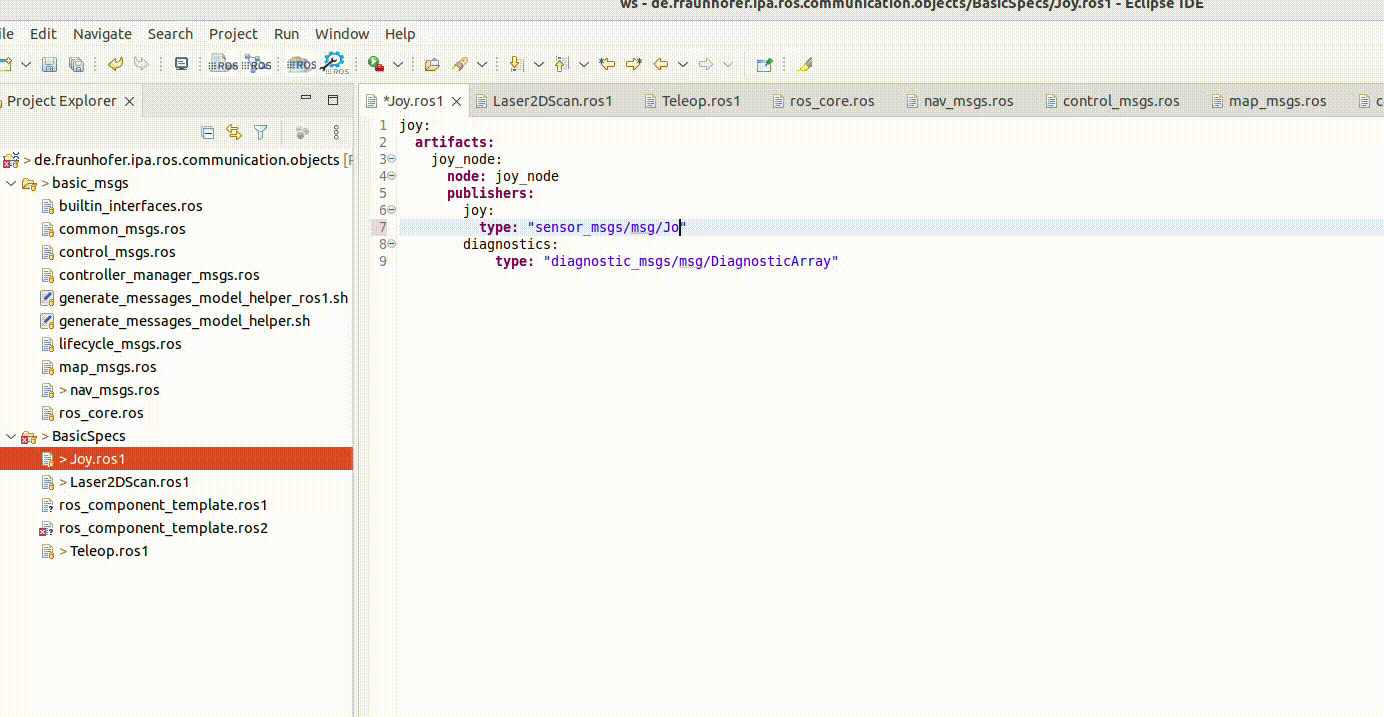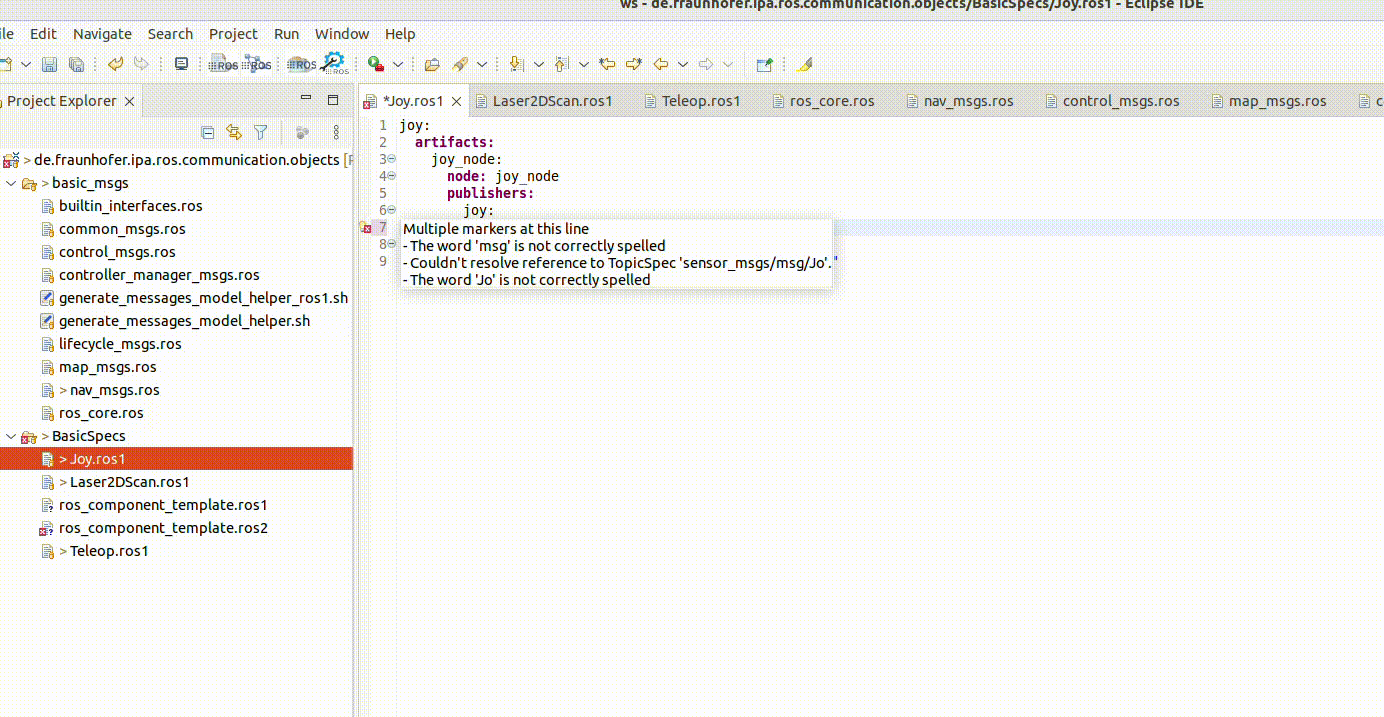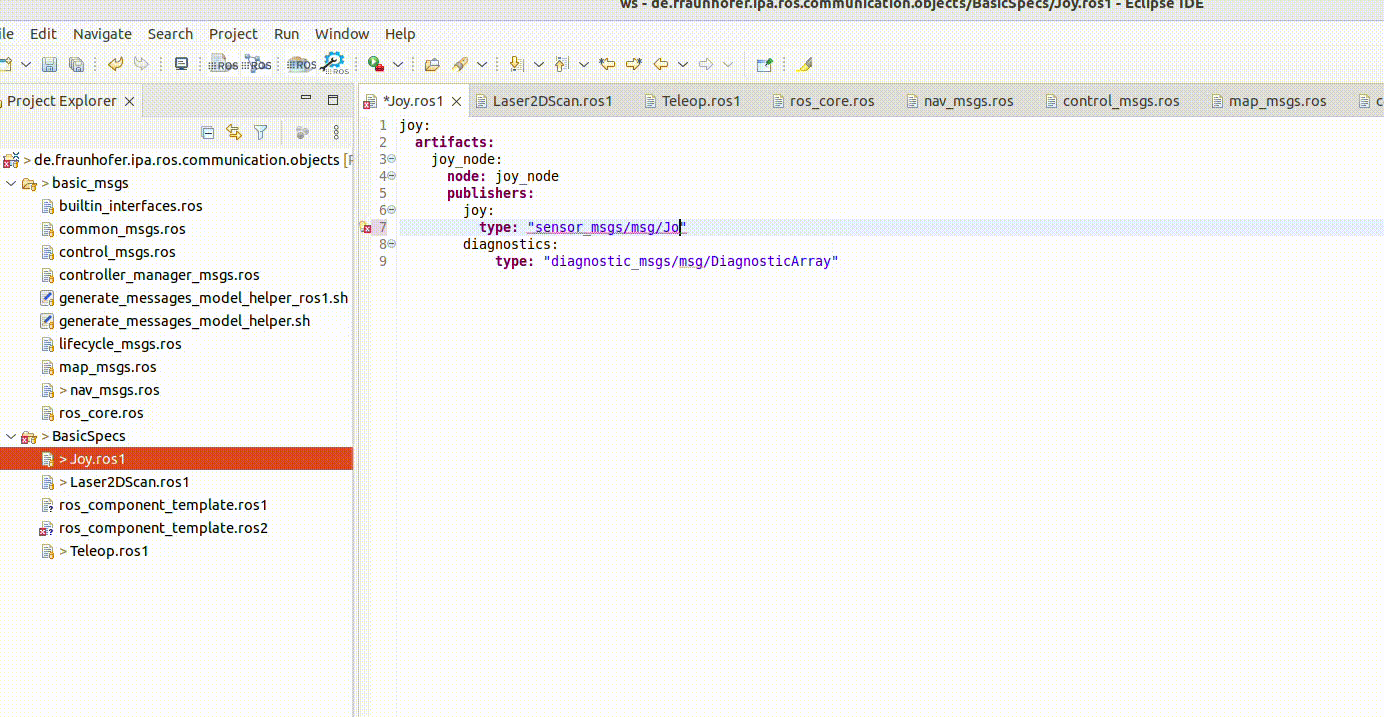
It incorporates also the auto-complete function. This is available by pressing Ctrl + the space bar:
In the tutorials you will be guided to try all of these features.